Why Lean Production?
- 70% of production effort time is considered a loss and only 30% adds value
- 50% of human effort time in production could be avoided
- 70% - 90% of machine stops could be avoided if the operator could take care of his machine properly
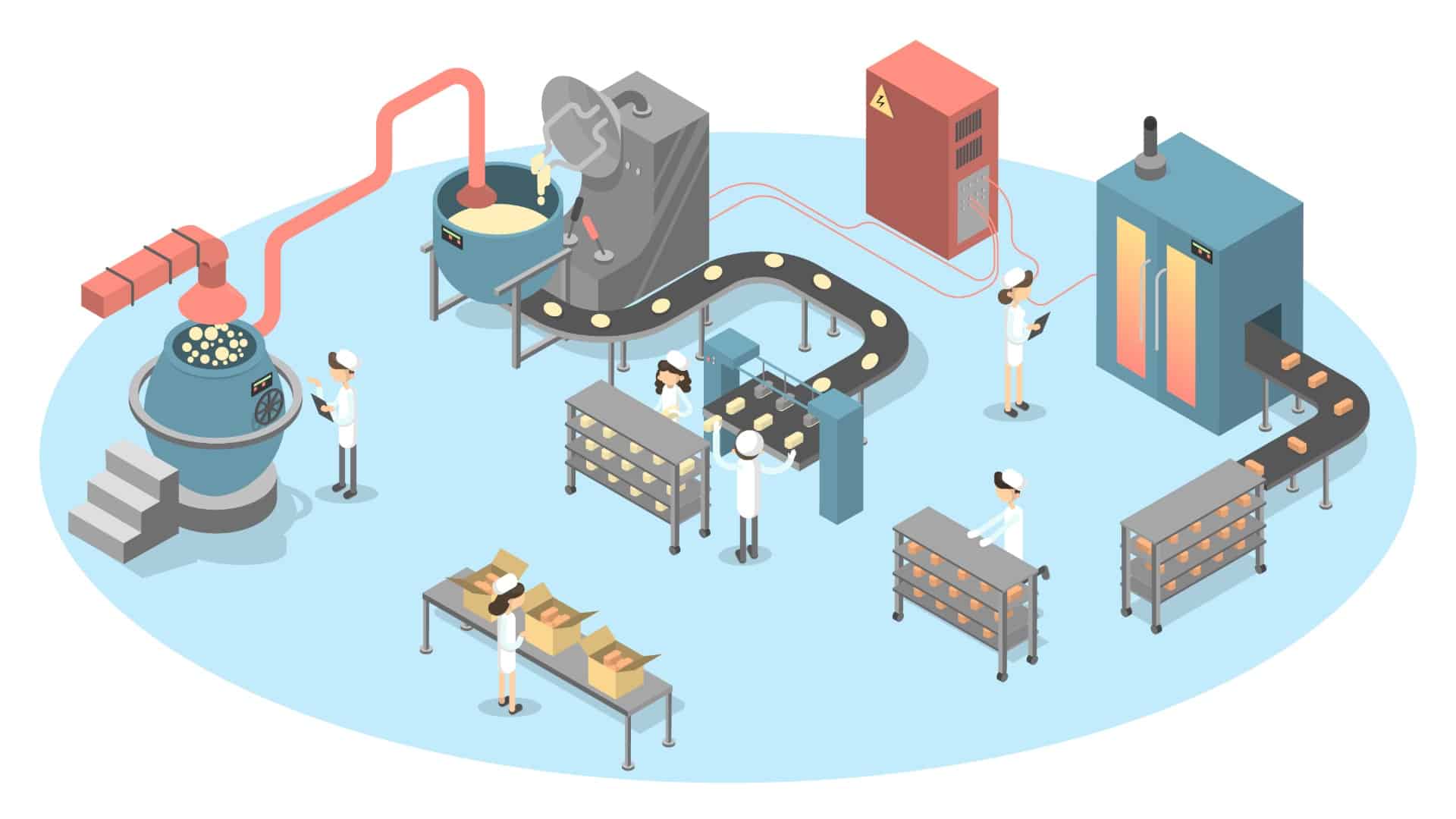
What is Lean Production
- Eliminate non added value processes
- Create a continuous flow in production with quick product changes and small batchesinstead of interruptions and waits.
- Produce according to the demand
- Continuous improvement process, with active participation of employees
Results
According to international reports, lean production can increase productivity by 27% and reduce:
Therefore, can increase:
(source MANUFACTURING ADVISORY SERVICE, UK)
How to eliminate waste
The basic action axes for the battle against the waste, as defined by the terms of lean methodology, are presented in the figure below.
Flow creation
Continuous Flow
- Line design
- Continuous flow by resource balance
Pull Production
- We produce what is needed, when is needed
Losses
Value added vs non-value added activities
- We identify value added and non-value added activities
Value stream
- We identify the value stream
Continuous improvement
Continuous improvement
- Eliminating losses
- Active participation of employees
- "Flow creation" eliminates many forms of waste, such as large inventories, waiting andtransportation.
- In "battle with losses" the goal is to shrink or eliminate all non-value added activities.
- "Continuous improvement" is a result of from a new way of thinking, where employees participate in proposals to reduce any form of waste in an ever-evolving process.
Tools / Techniques
BUSINESS ELEMENTS selects, adapts and applies the appropriate tools / techniques and offers solutions that lead to the optimization of unit production capacity.
Overall Equipment Efficiency, OEE
We measure productivity
OEE is the central indicator for measuring productivity. This indicator contains three components:
- Availability (e.g. out of order)
- Performance (e.g. low rate)
- Quality (e.g. scrap)
We design and implement measurement systems in order to create a way of progress monitoring and eliminate waste from the production process.
We organize actions for the continuous evaluation of OEE and the planning of improvement actions.
Value Stream Map (VSM)
We reveal the improvement margins
Value Stream Mapping (VSM) is one of the main tools for tracking losses and identifying improvement margins. This is a technique used to macroscopically map the flow of materials and information required in the production chain.
With the VSM display, we quantify the current and future state of the processes and highlight the improvement opportunities.
Flow
We design production lines
The main component of lean methodology is flow. Lean Production proposes contrary to the traditional way, a flexible traction system, where demand directly determines the quantities produced. Processes are performed in a continuous flow, without interruptions or waiting, by balancing the execution rate of the processes. The lean theory promotes the simplification of programming systems by visually alerting the people that “run” the processes, to ensure complete control of the flow.
We turn a classic factory into a lean factory, through a revolutionary differentiation of how it works. Necessary steps for this conversion are:
- The study of the products flow through process phases and the calculation of resource usage (lean flow study)
- The production line design instead of similar machine departments
- The balancing of each line, i.e. the maintenance of a constant rate of production (takt) through all processes of the line
- The optimal layout definition that serves the flows
SMED
We reduce machine preparation time (setup)
We apply the SMED technique, which aims to minimize the setup time of the machines, through specific actions such as:
- Convert as many actions as possible into external (thus performed while the production process is in operation)
- Simplify equipment for quick disassembly and assembly (e.g. replacing bolts with buttons and levers)
- Eliminate unnecessary actions
- Create standard work instructions
We implement SMED actions during workshops with employee’s participation and we achieve improvement in change times at the level of 40%.
5s
We organize the workplace
We use the 5s technique, to reduce waste through workplace or storage reengineering, cleaning and standardization, with the following actions:
- Sort: Remove those that are no longer needed
- Set in order: Organize the rest of them
- Shine: Cleaning and inspecting the area
- Standardize: Create templates
- Sustainable: Regular implementation of standards
We implement 5s actions during workshops with employee’s participation and we form organized workplaces that achieve safer, more efficient and productive operation.
Total Productive Maintenance, TPM
We apply lean techniques to maintenance
TPM is a holistic approach to maintenance, focusing on active and preventive maintenance in order to maximize the operating time of the equipment. It is implemented through 8 action axes, known as TPM pillars.
- Autonomous maintenance
- Education and training
- Quality maintenance
- Early equipment management
- Planned maintenance
- TPM in administration
- Focused improvement
- Safety, health, environment
In order to apply TPM techniques, we emphasize the empowerment of organizations that contribute to the maintenance of their equipment, removing the distinct line between maintenance and production. We create a sense of ownership for the equipment and encourage employee participation.
kaizen
We promote continuous improvement
The word kaizen comes from the Japanese words Kai, which means “change” and Zen, which means “for better”.
We are shaping a new way of thinking for employees focusing on continuous improvement. Our goal is for employees to work actively together to make improvements in the production process, through a routine of small daily proposals to reduce any form of waste.
Six Sigma, 6σ
We implement Six-Sigma projects
Six Sigma is an international methodology, based on the measurement and statistical data processing for performance improvement and deviation reduction in a process that focus on a product, service or transaction. Unlike quality control methodologies, which have focused on detecting and correcting problems at various stages of a process, Six Sigma is a comprehensive study to recreate the process so that imperfections and errors do not arise.
The Six Sigma methodology is based on the implementation of five steps described internationally abbreviated as DMAIC:
- Define the problem
- Measurement of parameters
- Analysis of them
- Improvement of the status quo of the problem
- Control of the procedure
BUSINESS ELEMENTS applies the 6s study to reduce deviations in sizes with significant sensitivity, such as quality results or processes that must have a low error margin (e.g. in the field of health).



